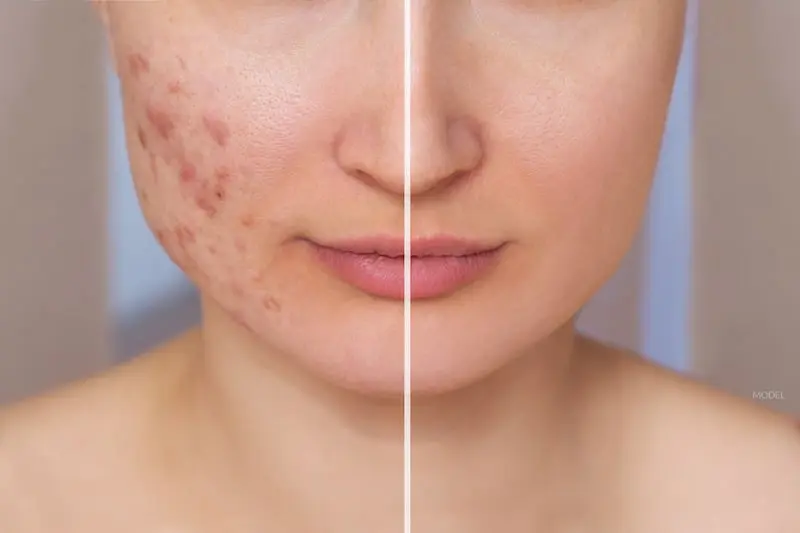
Acne: Acne is a skin problem that starts when oil and dead skin cells clog up your pores. Acne usually appears on your face, neck, chest, back, shoulders and commonly occurs in adolescence and in young adulthood. The major pathogenic factors involved are hyperkeratinization, obstruction of sebaceous follicles resulting from abnormal keratinization of the infundibular epithelium, stimulation of sebaceous gland secretion by androgens, and microbial colonization of pilosebaceous units by Propionibacterium acne, which promotes perifollicular inflammation.

Acne can be treated by various topical medications, oral drugs and other therapies like light therapy, chemical peels, extraction of white heads and black heads. A good and healthy lifestyle is also essential.
Scars: Scarring is a natural part of the healing process after an injury. Its appearance and its treatment depend on multiple factors. These are several different types of scars including:
Keloid scars: These scars are the result of an overly aggressive healing process. They extend beyond the original injury. Over time, a keloid scar may hamper movement. Treatments include surgery to remove the scar, steroid injections, cryotherapy or silicone sheets to flatten the scar.
Contracture scars: If your skin has been burned, you may have a contracture scar. These scars tighten skin, which can impair your ability to move. They may also go deeper, affecting muscles and nerves.
Hypertrophic scars: These are raised, red scars that are similar to keloids but do not go beyond the boundary of the injury. Treatments include injections of steroids to reduce inflammation or silicone sheets, which flatten the scar.
Acne scars: The types of acne scars include ice pick scars, rolled out scars and boxcar scars. Treatment options include chemical peels, TCA cross, microneedling fractional radiofrequency, subcision, microdermabrasion , dermaroller, LASERS, scar surgeries and fillers.
Skin pigmentation: The colour of skin and hair is mainly due to the amount of brown melanin pigment. Increase in melanin (hyperpigmentation or hypermelanosis) can be due to an increased number of pigment cells (melanocytes) or from increased production of melanin. Common causes for facial pigmentation include melasma, suntanning and freckles.

Melasma : Melasma is a chronic skin disorder that results in symmetrical, blotchy, brownish facial pigmentation. Most people get it on their cheeks, bridge of their nose, forehead, chin, and above their upper lip. Melasma is characterized by three location patterns (central face, cheekbone, and jawline). It also can appear on other sun exposed parts such as the forearms and neck. When it occurs in pregnancy it is called chloasma. Melasma is caused partly by sun exposure, genetic predisposition and hormonal changes. Prevention is primarily aimed at facial sun protection and sun avoidance. Treatment requires regular sunscreen application, skin lightening agents, chemical peels and LASERS.
Sun tanning : Sun tanning or simply tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight. Moderate exposure to the sun contributes to the production of vitamin D by the body, but excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays has negative health effects, including sunburn and increased risk of skin cancer, as well as depressed immune system function and accelerated aging of the skin. Some people tan or sunburn more easily than others. This may be the result of different skin types and natural skin color, and these may be a result of genetics. This can be alleviated at least to some extent by the prior application of a suitable-strength sunscreen, which will also hinder the tanning process due to the blocking of UV light. Treatment includes skin lightening agents, chemical peels and LASERS.
Freckles : Freckles are small flat brown marks arising on the face and other sun exposed areas. They are most often seen in fair skinned people, especially those with red hair, but they are an inherited characteristic that sometimes affects darker skin types as well. Skin pigment (melanin) is made by cells called melanocytes. They don't produce much melanin during the winter months, but produce more when exposed to the sun. The melanin is diffused into the surrounding skin cells, called keratinocytes. The colour of freckles is due to localised accumulation of melanin in keratinocytes. They are more prominent in summer but fade considerably or disappear in winter as the keratinocytes are replaced by new cells. As the person ages this type of freckle generally become less noticeable. Apart from sun protection, no particular treatment is necessary. Treatment includes skin lightening agents, chemical peels and LASERS.
Under eye dark circles: Are caused by multiple etiologic factors that include genetic/constitutional, dermal melanin deposition, post inflammatory hyperpigmentation, secondary to atopic or allergic contact dermatitis, anemia, stress, faulty habits, periorbital edema, superficial location of vasculature, and shadowing due to skin laxity, etc. Treatment includes correction of underlying causes, lightening creams and chemical peels .

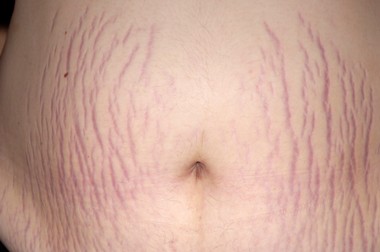
Stretch marks: also known as striae, are a form of scarring on the skin with an off-color hue. They appear to be caused by stretching of the skin. This is especially true when there is an increase in cortisone due to any hormonal imbalances as well. Over time they may diminish, but may not disappear completely. Stretch marks formed during pregnancy, usually during the last trimester, and usually on the belly, but also commonly occurring on the breasts, thighs, hips, lower back and buttocks, are known as striae gravidarum. Treatment includes topical creams, LASER treatment, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion.